Treatment of Adhesions
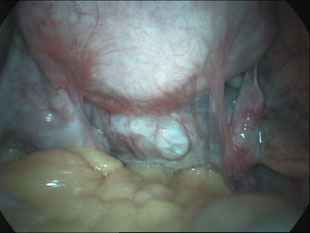
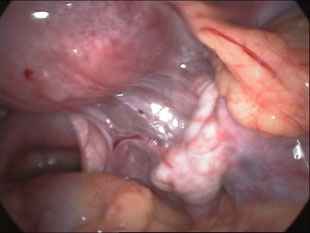
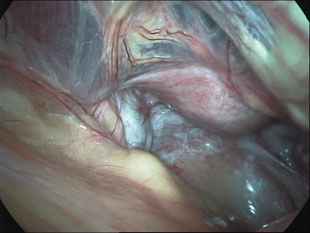
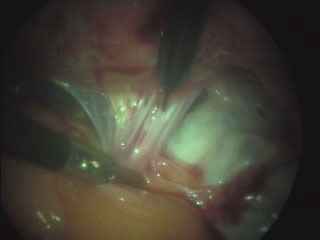
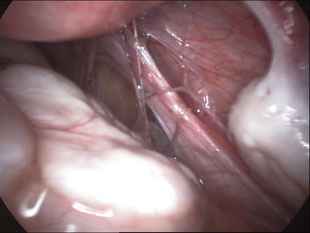
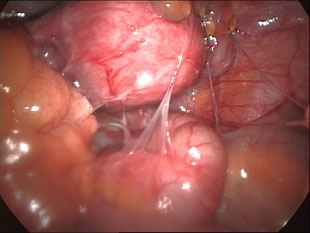
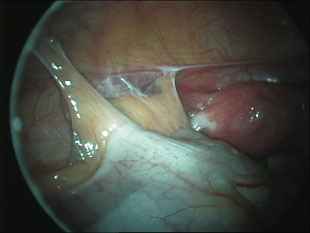
Adhesions within the abdomen and pelvis are treated by minimally invasive surgical techniques (laparoscopy). Lysis of adhesions can be performed as a part of other procedures (such as removal of ovarian cysts or fibroids), or as a procedure by itself. Although some believe that adhesions are a contraindication to performing laparoscopy, this belief is truly a misconception. Laparoscopy offers several advantages over laparotomy ("open" abdominal approach) in the treatment of adhesions. The laparoscope allows excellent visualization and magnification of the adhesions and the affected abdominal/pelvic organs. In addition, the CO2 gas which is used to inflate the abdomen provides a natural separation of the abdominal structures, allowing the adhesions to be clearly defined and effectively treated. The microsurgical principles which are employed with a laparoscopic approach also are much more effective in preventing the development of adhesions from the surgery itself.
Recovery from lysis of adhesions is fast as patients are usually discharged from the hospital within 24 hours and a return to normal daily activities can be expected within 1-2 weeks.
{multithumb}
Adhesions